Recent studies have amply documented that aging remains the most significant risk factor for major chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, tumors, metabolic diseases, and musculoskeletal diseases. The accumulation of senescent cells in tissues and organs with age is an important driving force for aging. Although senescent cells are in a permanent state of cell cycle arrest, they have high metabolic activity with a large number of secretions of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and extracellular matrix degradation proteins. This phenotype is also known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), which directly lead to progressive degeneration in tissues and organs. Eliminating senescent cells or reducing SASP is a potentially powerful anti-aging intervention.
On December 30, 2023, a research article produced by Haiteng Deng’s group in the School of Life Sciences was published in Redox Biology. The study, "Flavonoid 4,4'-dimethoxychalcone selectively eliminates senescent cells via activating ferritinophagy" found that 4,4′-dimethoxychalcone activates ferritinophagy and ferroptosis, leading to selective clearance of senescent cells.
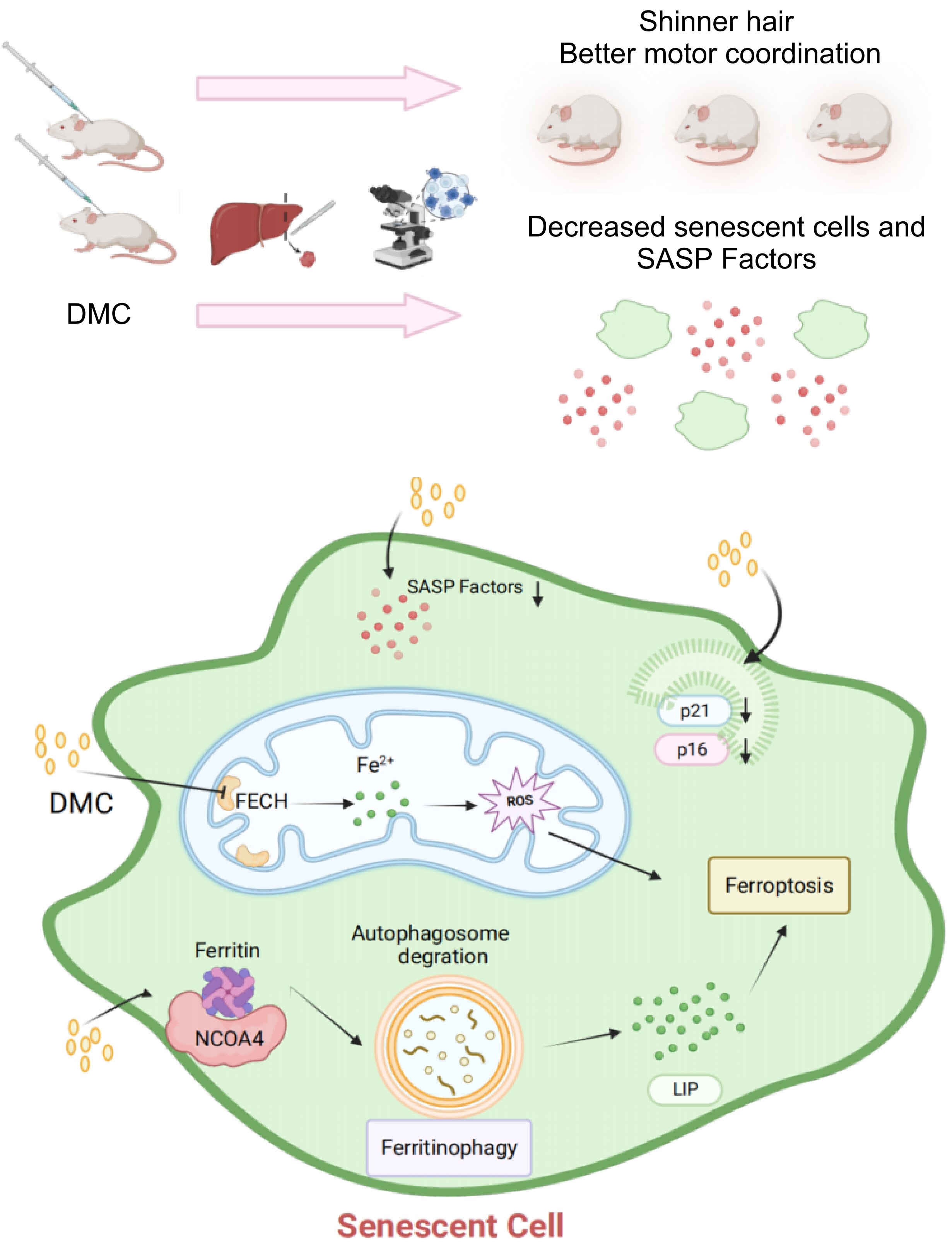
4,4′-Dimethoxychalcone (DMC) is the active component in Angelica keiskei koidzumi, known to be the "Immortality Elixir" that China’s First Emperor was seeking. By applying thermal proteome profiling, the authors found that DMC has multiple targets in cells, including ferrochelatase (FECH), and FECH is upregulated in multiple senescent cell models, suggesting that DMC can increase the level of ferrous ions in cells by binding to FECH. On the other hand, ferritin, the primary iron storage protein in mammalian cells, is upregulated in senescent cells. The authors found that DMC induces degradation of ferritin in cells, further increasing the labile iron pool. Indeed, the experimental results show that DMC treatment causes a threefold increase in the iron level in senescent cells, which induces ferroptosis in senescent cells. DMC also reduces the SASP phenotype of senescent cells. DMC alone or a combination of DMC and quercetin is more effective than the best known senolytics cocktail dasatinib and quercetin for eliminating senescent cells.
More importantly, the authors demonstrate that DMC alone or a combination of DMC and quercetin can significantly alleviate aging-related phenotypes in 20-month-old mice by reducing the number of senescent cells and SASP in liver tissue, by preventing hair loss, and by improving motor coordination. Taken together, the present study finds for the first time that ferroptosis is a novel form of cell death for senescent cells, and DMC is an effective senolytics.
Tianxiang Wang and Changmei Yang are co-first authors of this paper. Professor Haiteng Deng is the corresponding author. Other members from Deng's lab and staff members at the Protein Chemistry and Proteomics Facility of Tsinghua University contributed to an analysis of the data. This work was supported by NSFC and MSTC grants.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2023.103017
Editor: Li Han

