Quantum entanglement is a type of crucial resource in quantum networks. By distribution of quantum entanglement resources among multiple users, quantum networks could support various quantum information applications, such as quantum key distribution (QKD), quantum teleportation, distributed quantum computing and distributed quantum sensing. Introducing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) into quantum entanglement distribution networks can fully utilize the entanglement resources generated by broadband quantum light sources. However, due to the limited number of wavelength channels in the telecommunication band, the user number in a WDM-based network is constrained. The spatial division multiplexing (SDM) based on passive beam splitters can significantly enhance the user number of the network, but it requires compromises in network performance. Additionally, network routing control and reconfiguration are significant functions that quantum networks need to possess for practical applications. How to construct a large-scale, reconfigurable, and high-performance quantum entanglement distribution network remains a challenge to be addressed.
Recently, Professor Wei Zhang from Tsinghua’s Department of Electronic Engineering proposed a reconfigurable quantum entanglement distribution network based on a silicon photonic integrated four-wave mixing quantum light source. By introducing a pump management mechanism, the number of wavelength channels required for an N-user network is reduced to O(N) (compared to O(N²) in traditional WDM-based quantum entanglement distribution networks). This network also possesses strong capabilities on network reconfiguration while ensuring that each pair of user lines independently and utilizes a single entanglement resource. These features make this network architecture advantageous in terms of scalability, reconfigurability, and high performance.
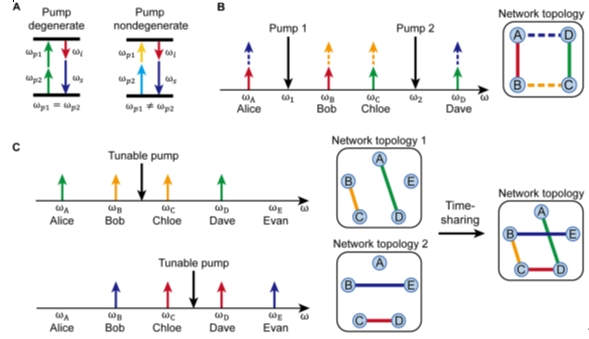
Fig. 1 The pump management mechanism of four-wave mixing sources for the quantum entanglement distribution network
The proposed network flexibly utilizes silicon waveguides to generate entangled photon pairs through spontaneous four-wave mixing (SFWM). When multiple pump lights are injected into the silicon waveguide, they simultaneously excite multiple degenerate and non-degenerate SFWM processes, resulting in photon pairs that exhibit complex frequency correlation characteristics in their spectra. By assigning photons of different frequencies to network users, a specific quantum network topology could be naturally formed among the users. When the frequencies of the pump lights change, the topology of the network also changes. This mechanism is referred to as "pump management." To demonstrate the potential application of this network, this work also showcases a fully connected entanglement-based QKD network with 10 users through pump management using three wavelength pump lights.
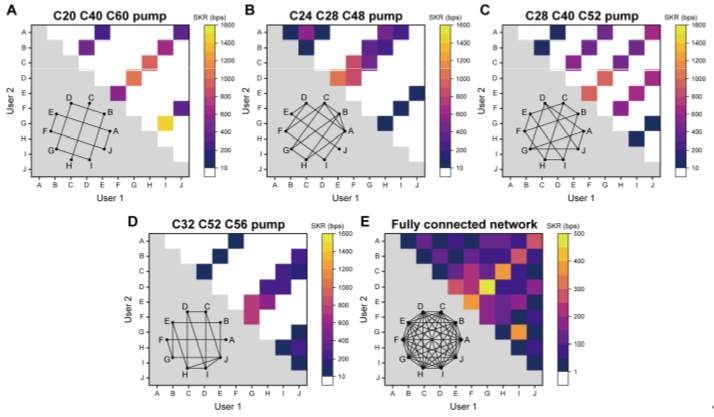
Fig. 2 The network topologies and experimental results of the fully connected entanglement-based QKD network with 10 users
On December 13, 2024, this work was published online in Science Advances under the title "Reconfigurable Entanglement Distribution Network Based on Pump Management of Spontaneous Four-Wave Mixing Source." Miss Jingyuan Liu, a PhD candidate from the Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, is the first author of the paper. Prof. Wei Zhang and Prof. Yidong Huang are the corresponding authors. This research used single photon detectors developed by Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIMIT, CAS). It was supported by the Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and National Key Research and Development Program of China.
Editor: Li Han

